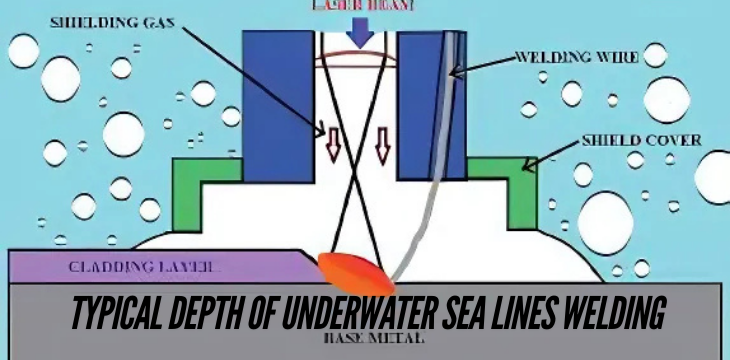
Underwater welding – it’s as fascinating as it sounds! But it’s not just about welding in water; it’s about a process that holds together the structural backbone of our offshore oil, gas, and even telecommunications industries. typical depth of underwater sea lines welding When you think of underwater sea lines welding, you might imagine daring divers, massive undersea pipelines, and dark, cold depths. And you’d be right! Welding underwater involves specialized skills, technology, and, of course, the ability to work at impressive depths where most people wouldn’t dare go.
One crucial question often asked in this field is: What’s the typical depth of underwater sea lines welding? It’s a reasonable question because depth influences everything in underwater welding, from the tools used to the welder’s safety. In this article, we’ll explore the typical depth, the techniques, the challenges, and the types of projects that require underwater welding. So, let’s get ready to dive deep!
What is Underwater Sea Lines typical depth of underwater sea lines welding?
Underwater welding is the process of joining two or more metal parts together beneath the water’s surface. It’s used primarily for repairing or constructing sea pipelines, offshore oil rigs, ship hulls, and other submerged metal structures. Unlike surface welding, where welders work in relatively controlled conditions, underwater welding presents a host of unique challenges, not least of which is the depth itself.
Underwater welding happens in two main ways:
- Wet Welding: Welding takes place directly in the water.
- Dry Welding: Welding occurs in a hyperbaric chamber placed over the weld site to keep water out.
Each method has its pros and cons, and choosing the right one largely depends on the depth and nature of the job.
Typical Depth of Underwater Sea Lines Welding: How Deep Do They Go?
So, how deep does underwater welding actually go? The typical depth of underwater sea lines welding depends on a few factors, including the type of weld, the tools and safety gear used, and the divers’ skills. However, as a general guideline:
- Most underwater welding for sea lines typically happens at depths between 30 and 200 feet.
- Specialized deep-sea projects can require welding down to depths of up to 1,000 feet or more.
Factors That Influence typical depth of underwater sea lines welding
The depth at which underwater welding occurs can vary significantly based on the type of sea lines and the specific project requirements. Here’s a breakdown of some key factors:
- Project Needs: Some repairs or constructions require work at extreme depths, while others happen closer to the shore.
- Equipment Limitations: Not all welding equipment is designed to work effectively or safely at extreme depths.
- Diver Skills: Deep-sea welding isn’t for beginners. Welders must be certified, experienced, and prepared to handle the unique demands of deep water.
- Environmental Conditions: Ocean currents, water temperature, and pressure increase with depth, all of which impact welding techniques and safety.
While 30 to 200 feet covers the most common jobs, the deeper you go, the more complex and dangerous the task becomes. Let’s explore why.
Challenges of typical depth of underwater sea lines welding
Underwater welding at depth is no walk in the park – it’s a complicated, highly specialized field requiring skill, patience, and, let’s face it, a bit of bravery. Here’s why:
1. Pressure: The Big Deal Down Below
At depths below 200 feet, the pressure becomes intense. Every additional 33 feet of water adds another atmosphere (or 14.7 psi) of pressure. For divers, this means breathing becomes more difficult, and the physical strain on the body increases. Plus, equipment must be rated to withstand these high pressures, which isn’t always easy (or cheap) to acquire.
2. Temperature: Freezing Down There!
Deep water is cold. Really cold. Working in temperatures near freezing can limit a diver’s mobility, affect concentration, and even cause hypothermia if not adequately protected. Divers wear specialized suits, but even those can only protect against the cold for so long.
3. Visibility: Or Lack Thereof
The deeper you go, the darker it gets. Sunlight doesn’t penetrate far beyond 650 feet, so welding at extreme depths often requires artificial lighting. Even then, silt and marine life can cloud visibility, making a precise weld difficult. Try welding blindfolded, and you’ll get the idea!
4. Marine Life: It’s Their Territory!
At depths where humans rarely venture, marine creatures are naturally curious. Sharks, jellyfish, and even the occasional giant squid may inspect welding work, adding a bit of suspense to the job!
How Is typical depth of underwater sea lines welding? The Techniques Behind the Scenes
Welding underwater, especially on sea lines, requires advanced techniques. Here are the primary ones used:
Wet Welding
This is the most common type of underwater welding. Wet welding involves using a specially coated electrode that can withstand exposure to water. The welder completes the job using shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) techniques.
- Advantages: Cost-effective and quick setup.
- Challenges: Higher risk of weld failure due to hydrogen embrittlement (where hydrogen atoms infiltrate the weld, weakening it).
Dry Welding (Hyperbaric Welding)
In dry welding, a pressurized chamber is placed over the weld area, pushing water out so the weld can be made in dry conditions. This approach is generally used at greater depths or for high-precision projects.
- Advantages: More reliable weld quality and reduced risk of embrittlement.
- Challenges: Complex setup and higher costs, plus the chamber needs to withstand extreme pressure.
Types of typical depth of underwater sea lines welding Projects
So, who’s hiring underwater welders to work on these sea lines, and why? Here are some typical projects that involve underwater sea line welding:
- Oil and Gas Pipelines: Constructing and repairing pipelines at sea is crucial for the oil and gas industry.
- Underwater Telecommunications Lines: These cables carry internet and communication lines across continents, requiring reliable welding.
- Ship Hull Repairs: Ships may sustain damage below the waterline, making underwater repair essential.
- Offshore Rig Construction: Welding is often needed to secure various metal structures on oil rigs.
FAQs: What You Need to Know About typical depth of underwater sea lines welding
1. How deep can underwater welders go?
- Most underwater welding occurs at depths between 30 and 200 feet, but specialized work can happen as deep as 1,000 feet, with significant challenges.
2. Is wet welding as effective as dry welding?
- Wet welding is effective for certain repairs but comes with a risk of hydrogen embrittlement. Dry welding, though more complex, is preferred for precision and safety.
3. How much do underwater welders make?
- Underwater welders can earn anywhere from $50,000 to $200,000 annually, with the exact pay depending on skill, experience, and depth of work.
4. What equipment is used in underwater sea line welding?
- Key equipment includes a waterproof welding machine, electrodes, pressurized dry chambers (for dry welding), and a specialized diving suit.
5. How dangerous is underwater welding?
- It’s considered one of the most hazardous jobs, due to risks like decompression sickness, electrocution, and potential encounters with marine life.
Conclusion
The typical depth of underwater sea lines welding varies depending on the project, equipment, and safety requirements, but most jobs fall within 30 to 200 feet below the surface. This vital work keeps pipelines, communication lines, and offshore rigs operational, and while it’s challenging, it’s also highly rewarding for those with the right skills and training.